A stem cell transplant replaces diseased stem cells with healthy ones and is often used to treat this form of cancer.
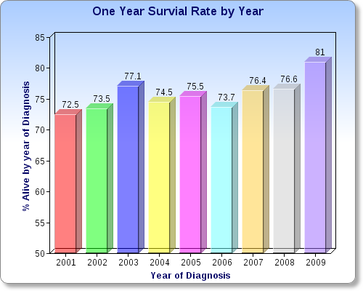
Multiple myeloma survival rate with stem cell transplant.
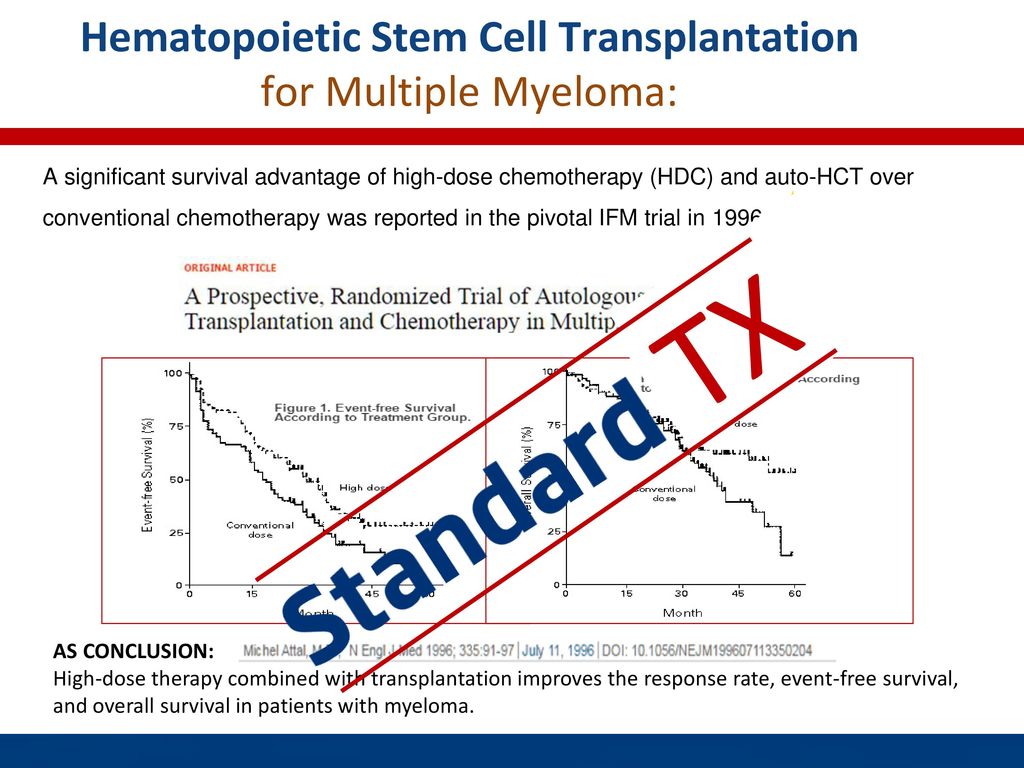
Patients with multiple myeloma live longer without their disease progressing if they get a stem cell transplant compared with patients who received chemotherapy alone.
See drug therapy for multiple myeloma stem cell transplants sct can be autologous or allogeneic.
We here analyze factors influencing survival in 865 newly diagnosed mm patien.
Multiple myeloma isn t considered curable but symptoms wax and wane.
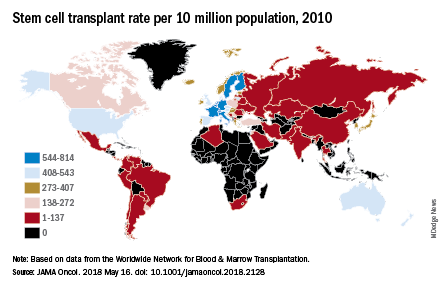
Stem cell transplant is commonly used to treat multiple myeloma.
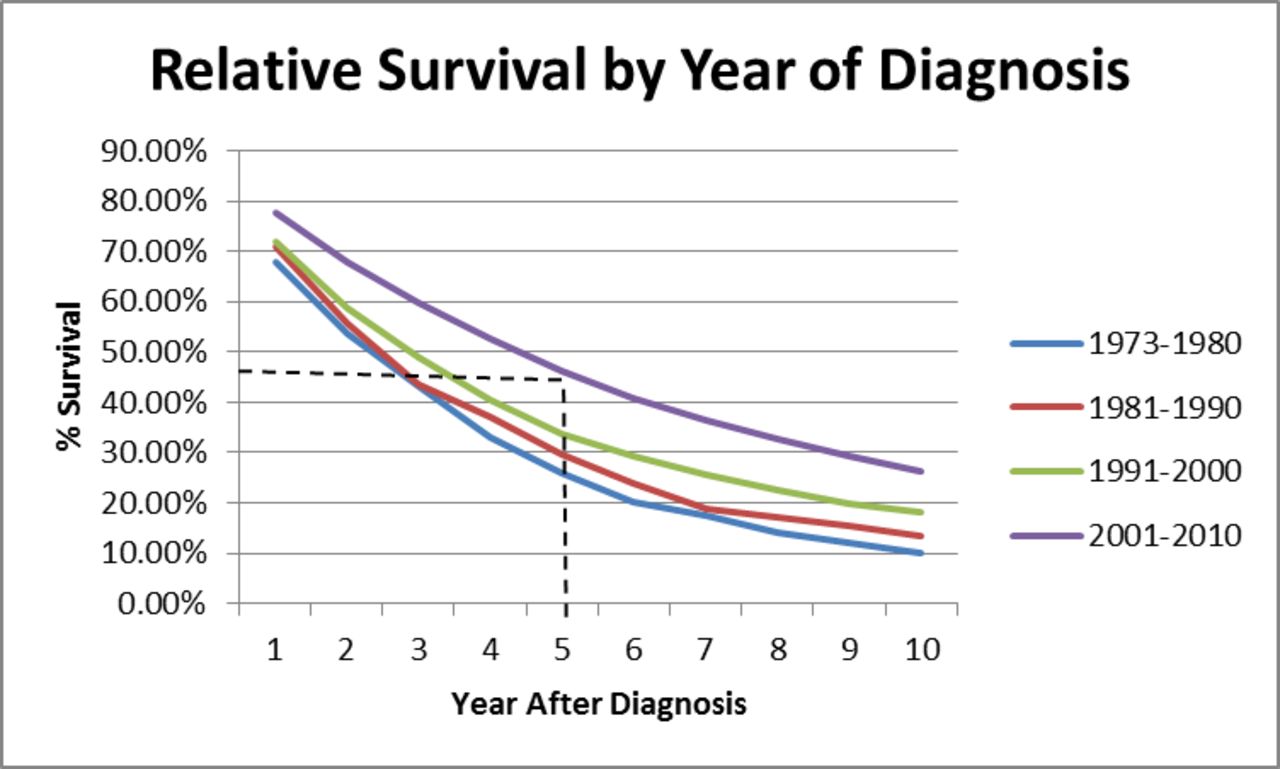
For example if the 5 year relative survival rate for a specific stage of multiple myeloma is 60 it means that people who have that cancer are on average about 60 as likely as people who don t have that cancer to live for.
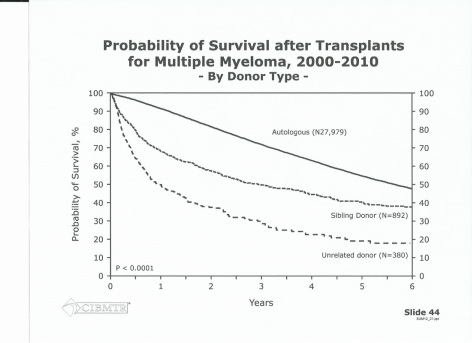
Autologous stem cell transplantation autosct has an important role in the treatment of patients with symptomatic multiple myeloma mm.
A relative survival rate compares people with the same type and stage of cancer to people in the overall population.
Multiple myeloma survival rate after stem cell transplant.
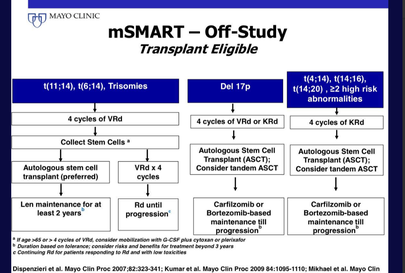
Treatment options for myeloma have expanded in.
Before the transplant drug treatment is used to reduce the number of myeloma cells in the patient s body.
There can be a long period of dormancy that could.
Findings from a phase 3 clinical trial note that patients with multiple myeloma who receive upfront autologous stem cell transplant asct typically live longer without disease.
All things considered while the autologous transplant can make the myeloma go away for a period of time even years it does not cure the growth and inevitably the myeloma back.
The high doses of chemo or radiation used to treat a multiple myeloma relapse can kill the stem cells in your bone marrow.
In some cases a bone marrow or stem cell transplant is an option.
A person with multiple myeloma is likely to have a low blood count.
To protect them your doctor removes stem cells.
Older patients and those with low risk disease show the greatest gains over time while people with high risk factors showed the least change its researchers said.